Prototype PCB Assembly Guide - Ukrainian
Winnie King
In the fast-evolving world of electronics, speed, accuracy, and reliability are non-negotiable. Whether you are a startup developing a groundbreaking IoT device or an established company iterating on existing technology, the journey from idea to market-ready product hinges on one critical phase: Prototype PCB Assembly.
What Is Prototype PCB Assembly?
Prototype PCB Assembly refers to the process of assembling electronic components onto a printed circuit board (PCB) for testing and validation.
Why Prototyping Matters
- Design errors caught during PCB Sample testing can prevent expensive redesigns.
- Component placement issues revealed early improve yield rates.
- Firmware and hardware can be developed and debugged simultaneously.
The Role of PCB Sampling in Product Development
1. Proof of Concept (PoC)

At the earliest stage, a basic PCB Sample helps demonstrate that the core idea works.
2. Functional Testing
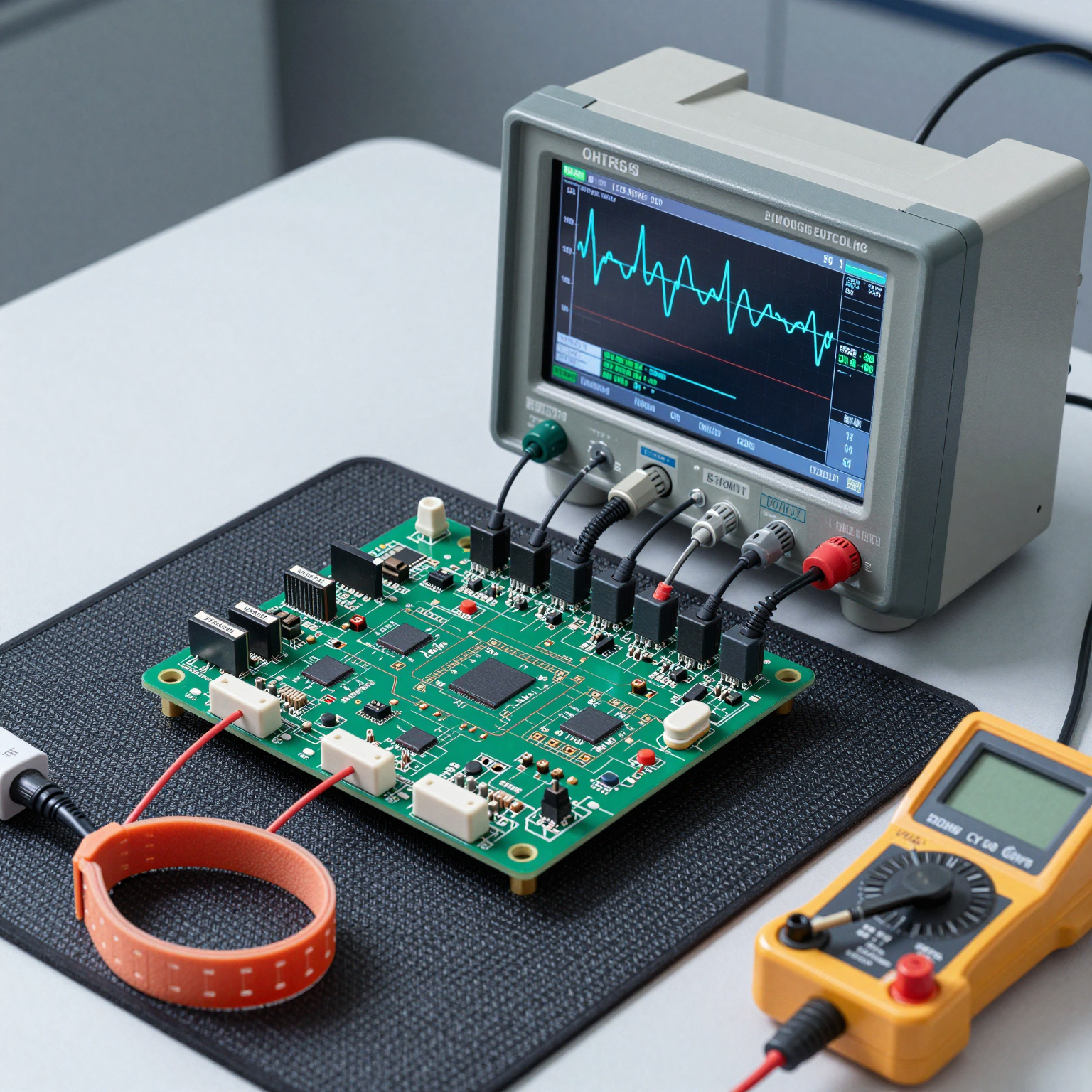
Refined prototypes undergo rigorous functional testing.
3. Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
During PCB Sampling, manufacturers analyze the layout for potential production issues.
4. Client and Stakeholder Review
Physical prototypes provide tangible evidence of progress.
Key Steps in the Prototype PCB Assembly Process
Step 1: Design Finalization
- Schematic capture
- PCB layout using tools like Altium Designer, KiCad, or Eagle
- Generation of Gerber files and BOM
Step 2: Component Sourcing
Reputable manufacturers offer electronic component sourcing services.
Step 3: PCB Fabrication
Quick-turn services deliver boards in 24-72 hours.
Step 4: Assembly Method Selection
- Surface Mount Technology (SMT)
- Through-Hole Technology (THT)
Read our guide on SMT vs through-hole assembly.
Step 5: Soldering
After component placement, soldering follows with AOI inspection.
Step 6: Testing and Validation
- Power-on tests
- In-circuit testing (ICT)
- Functional testing
Benefits of Professional Services
Faster Time-to-Market
Experienced manufacturers have streamlined workflows.
Higher Quality
Professional facilities adhere to strict quality standards (IPC-A-610 Class 2/3).
Access to Advanced Technologies
See our article on BGA assembly challenges.
Scalability
A good partner can transition to high-volume production.
Choosing the Right Partner
Turnaround Time
Some companies deliver assembled boards in 5-7 days.
Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)
Ensure the manufacturer supports low MOQs.
Technical Capabilities
Explore PCB manufacturing capabilities.
Support
Common Challenges
1. Incomplete BOM
Always check part numbers, values, and package types.
2. Poor Layout Practices
See PCB surface finishes guide.
3. Overlooking Test Points
Design test points early.
4. Ignoring Thermal Management
Ensure adequate copper surfaces and heatsinks.
Conclusion
Prototype PCB Assembly is a strategic investment in your products success.
Connect with a trusted PCB assembly manufacturer and start your journey from prototype to product.
