Flexible PCB Design: Key Considerations and Best Practices
SUNTOP Electronics
In today’s rapidly evolving electronics landscape, flexibility is no longer just a feature—it's a necessity. As devices become smaller, lighter, and more complex, traditional rigid printed circuit boards (PCBs) are often insufficient to meet modern design demands. Enter Flexible PCBs—a transformative solution enabling compact, lightweight, and highly reliable electronic systems.
At SUNTOP Electronics, a leading PCB manufacturing services provider, we specialize in delivering high-performance flexible PCB solutions tailored to industries ranging from medical devices and aerospace to consumer electronics and automotive systems. Whether you're developing a wearable health monitor or an advanced drone control system, understanding the nuances of Flexible PCB Design is critical to ensuring product success.
This guide explores the key considerations and best practices that engineers and designers should follow when working with flexible circuits, with insights grounded in real-world PCB Manufacturing experience.
Why Choose Flexible PCBs?
Before diving into design specifics, it’s important to understand why flexible PCBs have become so indispensable.
Advantages of Flexible Circuits
- Space and Weight Reduction: Flex PCBs can be bent, folded, and shaped to fit into tight enclosures.
- Improved Reliability: Fewer interconnects and connectors reduce failure points.
- **Dynamic Flex
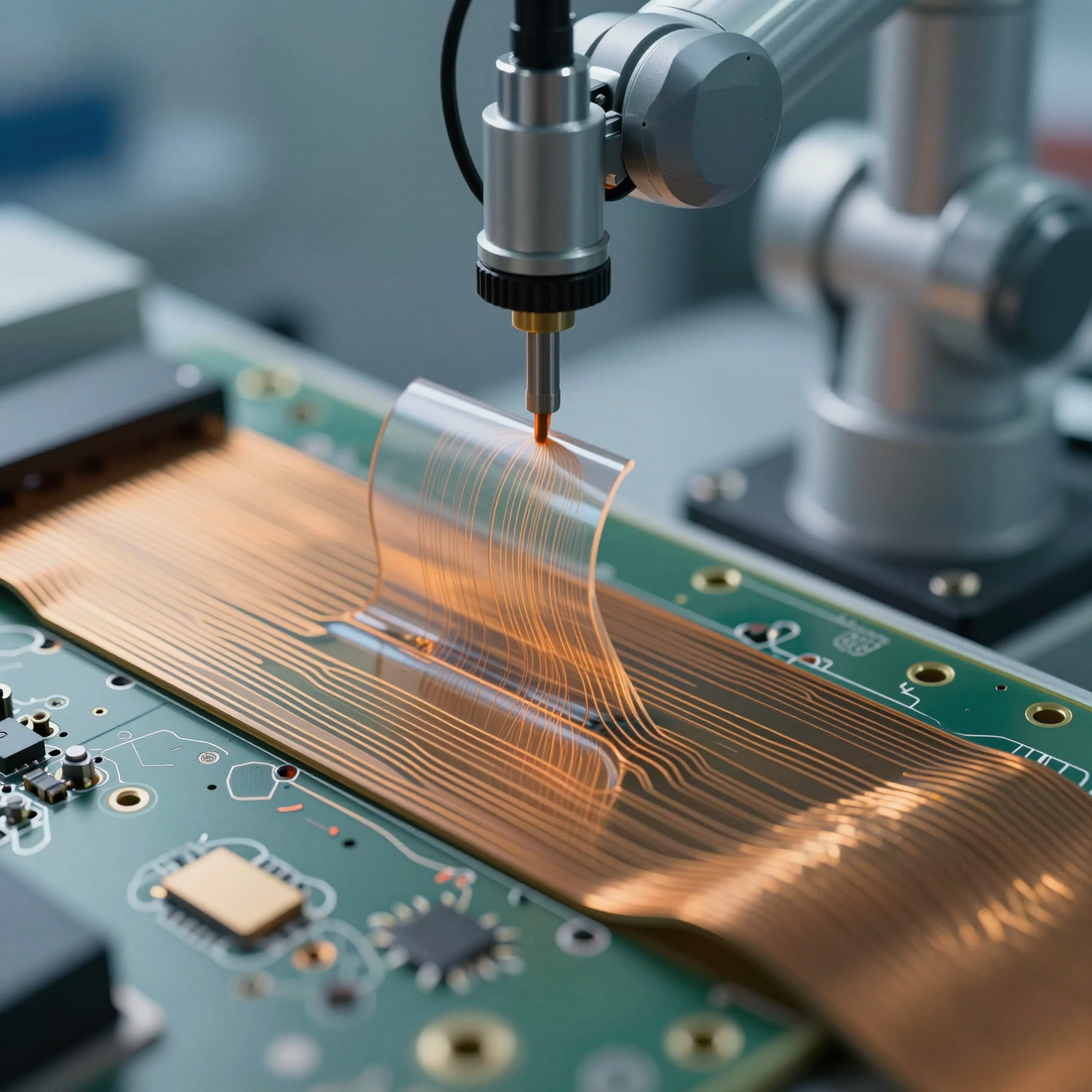
ing Capability**: Ideal for applications requiring repeated movement (e.g., printer heads, camera modules).
- Enhanced Thermal Management: Polyimide substrates offer superior heat resistance.
- Design Freedom: Enables 3D packaging and curved form factors not possible with rigid boards.
These benefits make flex circuits ideal for next-generation products where miniaturization and reliability are paramount.
Key Design Considerations for Flexible PCBs
Designing a flexible PCB isn’t simply about replacing a rigid board with a bendable one. It requires careful planning and adherence to specific guidelines to ensure manufacturability, durability, and performance.
1. Define the Bend Requirements Early
One of the first questions to answer is: Will this flex circuit be static or dynamic?
- Static Flex: The board bends once during installation and remains fixed. Less stringent design rules apply.
- Dynamic Flex: The board will bend repeatedly over its lifetime (e.g., flip phones, robotic arms). Requires tighter controls on materials, trace routing, and bend radius.
The minimum bend radius is typically specified as a multiple of the total stack-up thickness. For example:
- Static: 10x thickness
- Dynamic: 20x thickness or more
Ignoring these limits can lead to cracked traces, delamination, or via failures.
2. Material Selection Matters
The choice of substrate and cover layers significantly impacts performance.

**: Most common material due to excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and flexibility.
- Adhesive vs. Adhesive-less Laminate: Adhesive-less constructions offer better flexibility and reliability but are costlier.
- Copper Type: Rolled annealed copper is preferred for dynamic applications due to higher ductility compared to electro-deposited copper.
Work closely with your PCB manufacturer to select materials based on environmental conditions, expected lifespan, and mechanical stress.
3. Stack-Up Planning and Layer Transitions
Unlike rigid PCBs, flex designs must account for transitions between rigid and flexible sections—commonly known as rigid-flex PCBs.
Key tips:
- Use staggered vias instead of aligned ones across flex-rigid interfaces to reduce stress concentration.
- Avoid placing components directly over transition zones.
- Maintain symmetry in layer construction to prevent warping.
A well-planned stack-up ensures signal integrity, mechanical stability, and ease of assembly.
4. Trace Routing and Conductor Geometry
Routing conductors on flexible substrates requires special attention:
- Avoid 90° Angles: Use curved or mitered corners to minimize stress and risk of cracking.
- Increase Trace Width at Vias: Prevent necking effects that could lead to fractures.
- Use Teardrops: Reinforce connections between pads and traces.
- **Route Perpendicular
to Bend Lines**: Never route traces parallel to the direction of bending—this increases strain on copper.
Proper layout techniques enhance both electrical performance and mechanical longevity.
5. Component Placement and Solder Joints
Mounting components on flexible circuits introduces unique challenges.
- Stiffeners: Add FR4, polyimide, or metal stiffeners under connectors or heavy components to provide support during assembly and use.
- Keep Components Away from High-Stress Areas: Especially near bend zones or fold lines.
- Use Rounded Pads: Reduce stress concentration at solder joints.
Also consider whether surface mount technology (SMT) or alternative attachment methods like anisotropic conductive film (ACF) are appropriate.
Best Practices in Flexible PCB Design
Beyond basic considerations, following industry-proven best practices can dramatically improve yield and reliability.
1. Collaborate Early with Your PCB Manufacturer
Engage your PCB fabrication partner during the initial design phase. Many issues—like impedance mismatches, non-standard materials, or unmanufacturable geometries—can be caught early through design for manufacturability (DFM) reviews.
At SUNTOP Electronics, our team offers free DFM analysis to help optimize your Flexible PCB Design before production begins.
2. Optimize for Impedance Control and Signal Integrity
High-speed signals on flex circuits behave differently than on rigid boards due to variable dielectric properties and thinner materials.
Best practices include:
- Using controlled impedance modeling tools.
- Maintaining consistent reference planes.
- Minimizing discontinuities in transmission lines.
For RF and high-frequency applications, refer to comprehensive resources on high-frequency signal integrity.
3. Specify Surface Finish Appropriately
Surface finish affects solderability, shelf life, and contact reliability.
Common options for flex PCBs:
- ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold): Offers flat surface and good wire bonding capability.
- Immersion Silver/Tin: Cost-effective but less durable.
- Hard Gold Plating: Used for edge connectors subjected to frequent mating cycles.
Each has trade-offs in cost, durability, and process compatibility.
4. Include Proper Documentation and Markings
Clearly define:
- Bend lines and keep-out zones.
- Stiffener locations and thicknesses.
- Reference designators and polarity markings.
Use silkscreen sparingly on flex areas; consider laser marking for precision.
The Role of PCB Sampling in Flexible Circuit Development
Even the most meticulously designed flex PCB can encounter unforeseen issues during manufacturing or assembly. That’s why PCB Sampling is a crucial step in the development cycle.
Why Prototype Before Full Production?
- Validate design functionality.
- Test mechanical fit and flexibility.
- Identify potential manufacturing defects early.
- Optimize assembly processes.
At SUNTOP Electronics, we offer rapid PCB Sample turnaround with full testing and reporting. This allows customers to iterate quickly and confidently scale to volume production.
Our streamlined sampling process includes:
- Gerber file review and DFM check.
- Material preparation and stack-up confirmation.
- Fabrication using precision laser drilling and etching.
- Electrical testing and visual inspection.
- Delivery of functional prototypes within days.
Early prototyping reduces time-to-market and prevents costly redesigns later.
How SUNTOP Electronics Supports Your Flexible PCB Needs
As a trusted PCB assembly manufacturer, SUNTOP Electronics combines cutting-edge technology with deep domain expertise to deliver end-to-end solutions—from concept to completed assembly.
Our Core Capabilities Include:
- Advanced Flexible and Rigid-Flex PCB Fabrication
- High-Density Interconnect (HDI) Technology
- Precision SMT and Through-Hole Assembly
- Electronic Component Sourcing and Parts Procurement
- Comprehensive QA Services Including AOI, X-Ray, and Functional Testing
We serve diverse sectors including healthcare, telecommunications, industrial automation, and IoT, supporting innovations that push the boundaries of what electronics can do.
Whether you need a single prototype or high-volume production, our agile manufacturing model adapts to your project’s scale and complexity.
Ready to Start Your Project?
If you’re designing a new product using flexible circuits, don’t go it alone. Partner with a manufacturer who understands the intricacies of Flexible PCB Design and PCB Manufacturing.
To learn more about our offerings, visit our page on PCB services or explore our full range of capabilities.
Need a custom solution? Get a PCB quote today and let our experts help bring your vision to life.
Conclusion
Flexible PCBs represent a cornerstone of modern electronic design, offering unmatched versatility and performance. However, their successful implementation hinges on thoughtful design, precise manufacturing, and rigorous validation.
By adhering to proven best practices—such as proper bend management, strategic material selection, and early collaboration with your manufacturing partner—you can overcome common pitfalls and unlock the full potential of flexible circuitry.
With SUNTOP Electronics by your side, you gain access to world-class PCB Manufacturing, rapid PCB Sampling, and integrated assembly services—all designed to accelerate innovation and ensure product excellence.
Stay ahead of the curve. Embrace flexibility. Build smarter.
